One fintech innovation that has made it easier for banks and fintech to collaborate is banking as a service (BaaS). BaaS is greatly impacted by the technological change and mobile-first strategy that have emerged in recent years. Customers have the option to choose the essential financial products and services and utilize them in accordance with their needs thanks to a BaaS platform.
Banking As A Service (BaaS): What Is It?
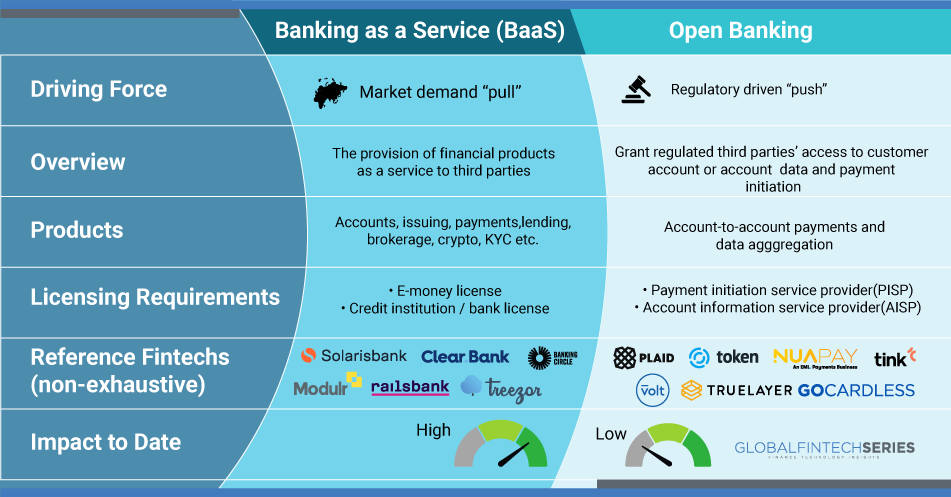
BaaS refers to the distribution of banking goods and services by outside distributors. BaaS services enable specialized interfaces and hasten their market entry by fusing non-banking companies with financial infrastructure. In other words, non-bank companies provide banking services without having to establish or buy their own banks. BaaS is a complete strategy that enables fintech companies and other third parties to connect with a bank’s technological infrastructure using APIs. This enables open banking services while assisting the firms in constructing cutting-edge financial services atop the regulated infrastructure of the providing bank. In recent years, there has been somewhat of a makeover in the banking industry. With fintech players entering the market, this transformation has become unstoppable. Financial services are changing in a way that they’re creating new products, channels, partnerships, and opportunities. Banking as a Service plays a significant role in this sphere.
Read: 5 Unconventional Ways To Make Money On Crypto In 2023
How Does The BaaS Value Chain Work?
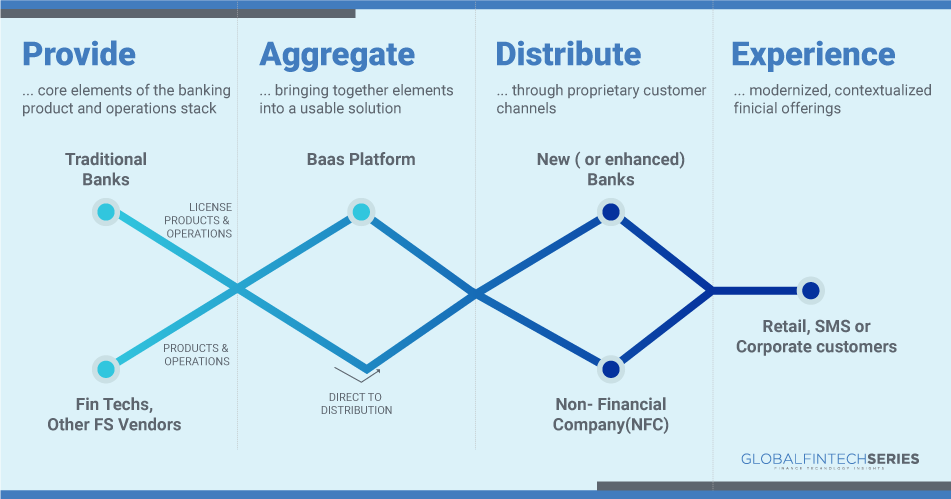
Banks are trying to catch up to the speed of fintech companies. Or, banks are partnering with fintech companies to innovate financial services. With APIs that connect banks and outside parties, banking as a service enables third-party organisations to use the existing financial services. These APIs enable non-financial businesses, programmers, developers, and fintech organisations to utilise certain banking services. Because of this, they are able to add their own features as a layer over the current banking services.
Read: Did You Know- 14 Bitcoin Facts
BaaS Statical Analytics:
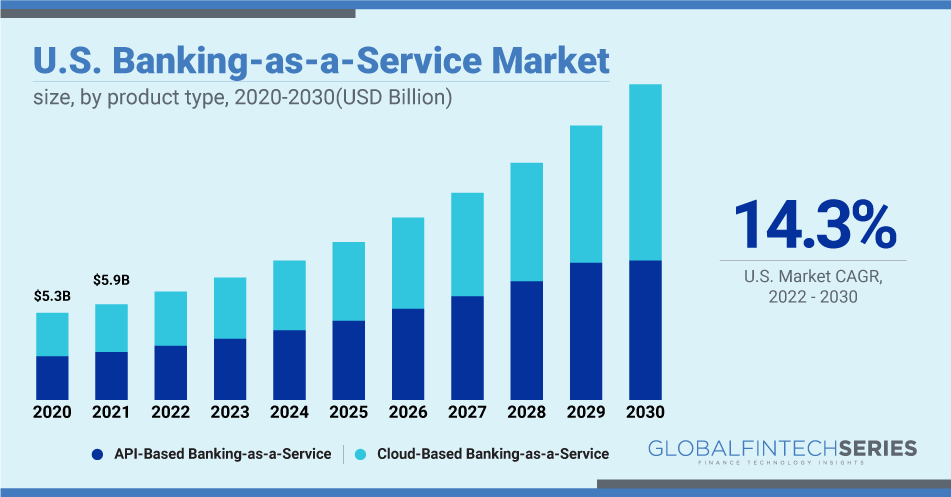
- 30% of clients say they’re thinking about changing banks.
- Customers have employed a Buy Now, Pay Later service in 42% of cases.
- 2x ROAA for banks that prioritize BaaS services
Recent Illustrations Of BaaS:
Deposit accounts have been introduced by numerous fintech platforms, including Dave, SoFi, and Betterment, as a complement to their initial primary service. These systems are enabled by white-label BaaS suppliers or bank relationships. Leading businesses and what they provide Treezor (payments), Bankable (digital banking, card programmes, e-wallets), Synapse (deposit accounts, loans, card programmes, cryptocurrency, payments), Cambr (deposit accounts, debit cards, payments), and GreenDot (deposit accounts, card programs, payments).
Banks: Conventional vs. Modern
Below is the graphical representation, we can easily differentiate between the traditional and new-age banks.
Benefits of BaaS For Fintech And Non-fintech Companies
- Low price: BaaS is a chance for a financial institution to contact more clients for less money. The outdated, expensive technology and procedures that make up the traditional banking business are used. A typical client acquisition expense is between $100 and $200. The price can range from $5 to $35 with a brand-new, greenfield BaaS technology stack.
- Banking online: Companies might put more effort into enhancing their offerings than fretting about bank integrations and licencing. These user-friendly, high-tech products may be preferable to conventional banking for its users. Additionally, they can create apps that let their clients to monitor their daily transactions, account balances, and saves. Remarkably, simple APIs make all of this possible.
- Provide Debit and Credit Cards: Using the Banking as a Service (BaaS) paradigm, non-banks can provide credit and debit cards to their customers. The Apple Credit Card is one example. Customers can access real-time updates on all of their transactions through an app. The customer’s account details and payments are shown in an approachable way.
- Provide Loans: Companies can use BaaS to offer loans to their customers. Companies can also offer clients the option to buy now and pay later. The client can choose their payment schedule in advance. To monitor their monthly EMI payments, they might utilize an app.
- Investment Services: In this department, staff members help clients automate their accounts and invest their money. They can help clients develop personalized investing strategies utilizing affordable index funds. Additionally, they have the ability to automatically rebalance the portfolio in line with the customer’s investment plan.
- Check the customer’s identity because unsuccessful payment transfers could harm a company’s reputation. Moreover, a business’s merchant account may be classified as a “high-risk merchant.” Verifying bank accounts can help to prevent payment transfer problems.
Read: Cybersecurity Timeline and Trends You Should Know before Planning for 2023
Advantages Of BasS For End-Customer
BaaS promotes financial services competition by allowing non-banks to provide fundamental banking services. As a result, innovation is pushed forward, and customers have access to more user-friendly products. Furthermore, it leads to increased financial transparency. Customers’ individual pain areas are the focus of third-party players. For example, a fintech company may solely specialize in business payouts.
This pressure has merely begun to increase as more technology companies enter the banking industry. Another aspect of this problem is the clientele. The new customer base is technologically advanced and demands instant access to financial information and goods. Unexpectedly, the countries with the youngest populations had the highest rates of fintech adoption. It’s possible that the frequency may reach 50%. Just even reaching that point of client pleasure is a big accomplishment. After all is said and done, working with a bank and adding financial products on top of that demand strict information security and consistency rules.
Read latest article: What Is Data Science?
BaaS’s difficulties
- Conventional banking institutions are progressively losing the advantage they once had over players in the fintech sector in terms of “client trust.” Considering that CIOs and CTOs do not follow technological trends. On the other hand, a lot of software companies are moving into the financial industry due to the high levels of client trust they have attained ( Eg. Apple Card).
- Financial institutions should be cautious when dealing with new associations because they may bring with them new hazards. To clearly define the roles and duties of the financial foundation and the wholesaler, a partnership governance model will be essential. The model should keep in mind a precise revenue share agreement, well-defined processes, and performance monitoring.
- BaaS additionally necessitates collaboration with numerous third-party players. Naturally, there are many similarities between the functional capacities. Furthermore, a lot of companies sell their goods under a white label, which is another name for private labelling. Customers may become confused as a result of this.
- Examining attentively at these considerations reveals a significant shift in the parties’ responsibility with regard to the future of BaaS. Banks may transition from being “makers” to becoming “assemblers,” or vice versa. This shows that they won’t limit their focus to the main banking services they provide. Financial institutions will, in general, collect value-added services from the services provided by their business partners.
Future Perspective for BaaS
The banking value chain is being reconfigured by banking as a service (BaaS), which is allowing for disintermediation and creating new opportunities for growth. BaaS refers to the distribution of banking goods and services by outside distributors. BaaS products are enabling new, customized offers and accelerating their time to market by combining non-banking enterprises with regulated financial infrastructure. A BaaS company is also adaptable and flexible, which makes it ideal for breaking into new markets before growing.