In this data-rich industry, every aspect of AI dynamics matters. There are several uses for AI in the financial sector. Perhaps the greatest benefit of artificial intelligence is the vast potential for automation it offers. Therefore, financial institutions may benefit from automation in many ways that boost production and efficiency. In addition, AI may take the place of people in certain tasks which reduces the likelihood of biases and other mistakes stemming from human emotions and mental faculties.
In this blog, we shall be limelighting AI and the financial services domain keeping in the loop the reports published by the World Economic Forum (WEF).
Read: Trust in Banking Explained With 10 Live Examples
Introduction
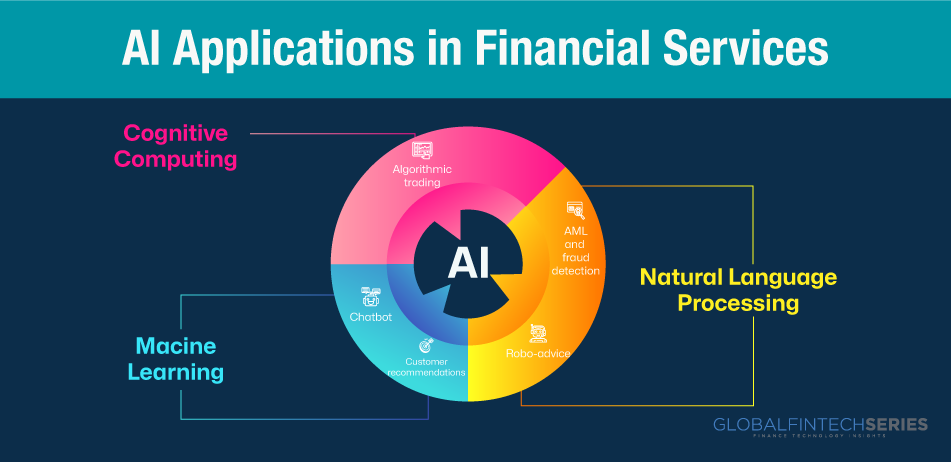
Here, Artificial intelligence gives a fresh ray of sunlight to the overall functionality of financial institutions. With the rapid and dynamic environment and technology on a horse ride, it is impertinent to notice how AI the most sought-after tech helps FI and how AI is magically transforming the operations of financial institutions. A study titled “The New Physics of Financial Services” was compiled. See below for a visual breakdown of how AI is being used in the banking and insurance industries.
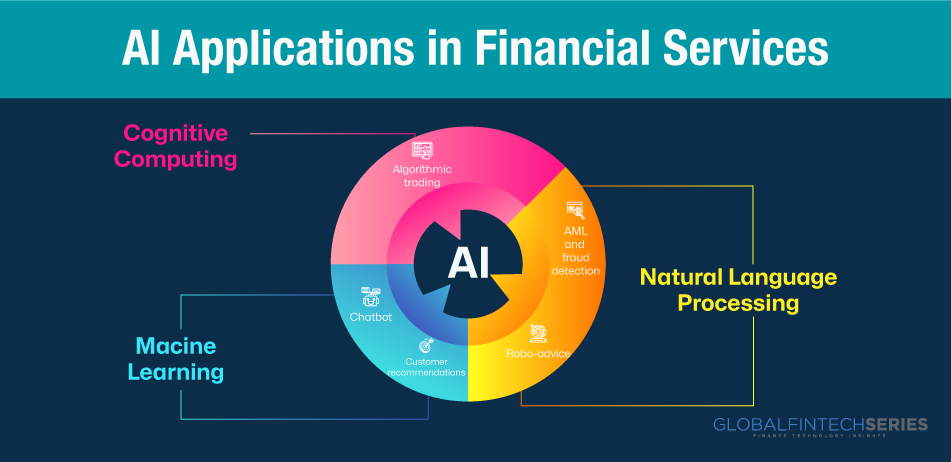
The use of AI in the financial sector is altering people’s interactions with money. AI aids the financial sector in a number of ways, including the acceleration and optimization of credit judgments, quantitative trading, and financial risk management. Additionally, the market is growing.
Exclusive Insights- AI Dynamics In Financial Services
 We had a one on chat discussion with Cigniti Technologies Chief Delivery Officer, Raghuram Krovvidy, below are his insights and thoughts in the domain of AP automation.
We had a one on chat discussion with Cigniti Technologies Chief Delivery Officer, Raghuram Krovvidy, below are his insights and thoughts in the domain of AP automation.Companies Using AI In Finance
Below are a few companies using AI in the finance domain, although there are plenty but here are the top 6 startups.
The new Physics of Financial services-World Economic Forum (WEF)
Here are some reactions from other organizations to the report by WEF that Deloitte cited.
Banking and insurance operations, including credit judgments and investment advice, will be profoundly impacted by AI in the back office. However, if we only look at the features that AI has to offer, we can miss the underlying change that is taking place. The requirements for creating a successful financial services business are continuously evolving due to AI. Mr. Ciobo, a partner at Deloitte in New Zealand, predicts that in the future, financial institutions will be constructed on a scale of data and the ability to leverage that data.
Many people, according to Banking Sector Lead Marco Ciobo, have seen the dazzling demos of AI helpers making appointments at restaurants and hair salons. And several New Zealand banks have already introduced or are in the process of introducing AI-powered customer support solutions. However, this is only the beginning. More public-private investment will be required, and an open and cooperative relationship between employees and management is essential if AI is to deliver on its promise. To effectively address these issues, he says, public and private stakeholders will need to work together to resolve regulatory uncertainties and manage the risks and opportunities presented by AI in financial services, even though regulators will continue to be responsible for addressing new questions about consumer protections and systemic risks.
Read the latest article: 10 Best Applications Of AI In Banking
Four key findings show how AI is revolutionizing financial organizations’ front- and back-office operations:
Financial institutions will be able to transform their centers of excellence into solutions by adopting Technology’s back-office tasks while being forced to outsource the majority of their other capabilities.
A new battleground for consumer loyalty – Financial institutions’ traditional ways of differentiating themselves, like price, accessibility, and speed, are disappearing. A new set of competitive characteristics is emerging as a result of AI that financial institutions can use to stand out to clients.
For instance, banks will be able to compete on the value supplied if they can personalize, recommend, and advise customers to optimize financial outcomes. They will be able to better retain consumers if they can engage users and get data through continuing, integrated interactions outside of the financial services industry. Financial institutions will be able to provide differentiated advice and enhance performance by curating ecosystems by combining data from multi-dimensional networks that include consumers, corporate clients, and third parties.
Self-driving finance: Financial advice is a component of every product but is frequently impersonal and general. Also, it frequently relies too heavily on the opinions of various customer service representatives. The provision of financial advice could change as a result of a self-driving financial vision that centers consumer experiences around AI.
According to this vision, people will increasingly interact with a single platform or agent who will suggest the kinds of things they should use and offer advisory services related to those items. Three important areas of AI support this vision: increasingly personalized recommendations based on data; empowered platforms that can compare and switch between products and services; and continual algorithmic improvement that will automate the majority of regular customer decisions.
Collective solutions to common issues – While AI increases the potential for competition, it also offers a powerful mechanism for cooperation due to the enormous value of shared datasets. On topics like fraud prevention and anti-money laundering measures, which are currently frequently conducted inefficiently and ineffectively, there is an enormous opportunity for inter-institutional cooperation.
Read: Unleashing The Power: How Tech Giants Harness Generative AI Chatbots
The quality, timeliness, and performance of non-competitive processes will be dramatically improved by collaborative solutions built on shared datasets, resulting in mutually beneficial operational efficiencies and enhancing the stability of the financial system.
Significant changes in the structure and regulation of financial markets are also examined, along with pressing issues that society must address.
- The market structure will be split in two as AI lowers the cost of search and comparison for consumers. This will increase profits for big companies and open up new opportunities for specialized and agile entrepreneurs.
- Uneasy data alliances: Managing alliances with rival institutions and potential rivals will be essential in an ecosystem where every institution is fighting for the diversity of data, but it carries significant strategic and operational dangers.
- The influence of data regulators: Data privacy and portability rules will influence how effectively financial and non-financial organizations can use AI, making them just as crucial to a company’s competitive positioning as traditional rules.
- Adapting talent strategies: The most difficult barrier to institutions using AI will be talent transformation, placing at risk the competitive positioning of companies and regions that fail to successfully transition talent along with technology.
- Emerging ethical conundrums: It is in the common interest of all world communities to reduce the risks and negative effects of rapid technological advancement. To address the ethical questions and legal ambiguity preventing institutions from adopting more revolutionary AI capabilities, AI will require a joint reexamination of principles and supervisory procedures.
Read: How Can Banks Stay Competitive With A Secured IT Security Infrastructure?
How did Financial services transform using AI?
Since the mid-1990s, the financial sector has seen a significant transformation. Digital technologies have had a profound impact on this region, and the rise of online banking and mobile money transfers has further digitized the financial sector. Nowadays, the most important factors in success are speed and ease of use. The majority of today’s workforce consists of members of Generation Z and Millennials, both of whom grew up used to having all the information they need at the touch of a screen.
Competition has intensified as online-only banks like Chime and Varo have emerged thanks to the digitalization of the banking sector. Even digital giants like Google aren’t immune to the allure of the retail banking market. The result is an increase in market volatility and competition. Companies need to innovate and adapt to be competitive in today’s market. Artificial intelligence (AI) is a technology that significantly benefits businesses by streamlining a great deal of their operations.
By 2030, AI is expected to have saved the banking sector almost $1 trillion.
More than a third (32%) of banks are already employing AI to create speech recognition and predictive analytics, enhance recommendation engines, and shorten response times. Every day, new use cases emerge, and businesses find new ways to put AI to work.
AI in financial services- Pros and Cons
The use of AI in financial services has various advantages. Automating processes, it can increase productivity and efficiency, lessen human biases and errors brought on by psychological or emotional factors, and enhance the quality and succinctness of management information by identifying anomalies or longer-term trends that are difficult to detect by conventional reporting techniques. These tools are especially useful when new laws, like the Markets in Financial Instruments Directive II (MiFID II) of the European Union, give senior management a greater obligation to evaluate and take into account better internal data.
Ignoring technological change in a financial system based upon technology is like a mouse starving to death because someone moved their cheese – Chris Skinner
Organizations may run into problems with AI applications if they don’t use adequate caution and caution. These include bias in the data used as input, the method and results of client profiling and credit scoring, and supplier chain due diligence risk. The data that has been utilized to train, test, retrain, update, and employ AI systems must be well understood by users of AI analytics. This is crucial when private analytics are constructed using third-party data and platforms or when analytics are offered by other parties.
Concerns exist over the propriety of utilizing big data for credit scoring and consumer profiling.
For instance, a British insurer abandoned a proposal in November 2016 to utilize personality analysis of social media postings to gauge the likelihood that first-time vehicle owners would drive safely and use the findings to determine the number of their insurance rates. The social media giant stated the project violated its privacy policies since it used data to make decisions about eligibility, including whether to approve or reject an application or how much interest to charge on a loan.
These issues often involve reputational hazards in addition to having legal and financial repercussions. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), for instance, grants EU residents the rights to information and access, correction, portability, the right to be forgotten, the right to limit the processing of personal data, and the prohibition of profiling. The ease with which people may refuse to have their data shared for consumer profiling is unknown, however. It is also unknown if people’s credit scores will be impacted by opting out, which may have an impact on the cost of insurance policies and whether they are eligible to apply for credit-based goods like loans.
According to a report by Hermes and BCLP, calls for the moral and responsible use of AI have been stronger as well, spurring worldwide momentum for the formulation of governance standards. Making the transition from ideas to practice, however, is the true issue.
Conclusion
The back-office-as-a-service paradigm that financial institutions are adopting shall enable these operations to continuously learn from and enhance customer data. As a result, capabilities advance more quickly, forcing competitors to use them in order to stay ahead of the competition.
Many sectors have been irrevocably altered by AI’s advent, and the technology’s enormous potential is without dispute. For this reason, it’s prudent to plan for the potential benefits of AI in the financial sector and anticipate its widespread adoption.
Read: What Is Data Science?
[To share your insights with us, please write to sghosh@martechseries.com]
