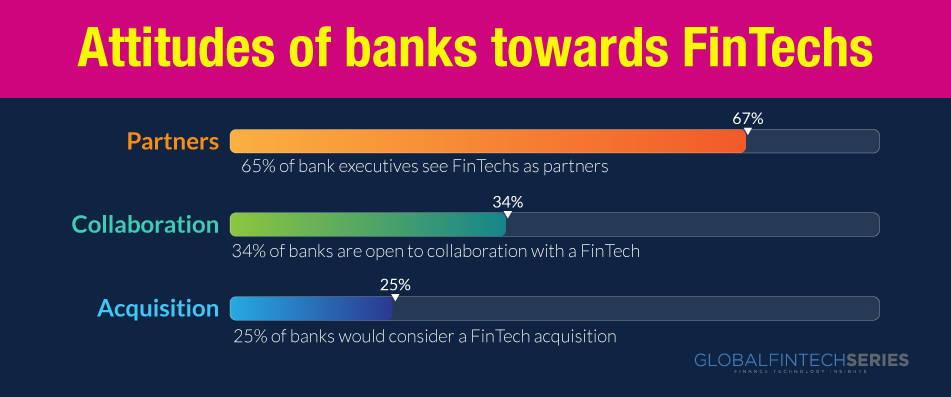
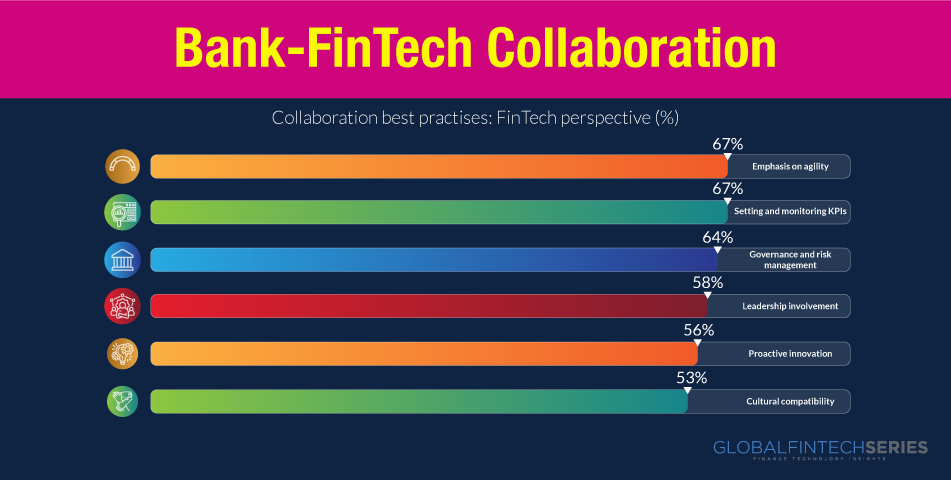
“Banks can partner with fintech to build an ecosystem where the size of the pie grows for the banks and third parties.” – Mike Henry, Scotiabank
Banks need to heavily invest in fintech solutions and implement digital strategies to keep up with the ever-changing competitive landscape. This blog has highlighted that it is difficult to compare fintech to traditional banking because each has its unique advantages. However, as the world evolves and new technology arises, fintech has become the most practical option.
The efforts of new fintech companies to set apart individual financial services have garnered the lion’s share of media coverage. When faced with this new challenge, how are financial institutions reacting?
They have been slow to respond to the upstart movement despite their money, intellect, and long history of invention. This article presents a bundle of ideas as to how fintechs are making banking institutions perform better and carving a niche for themselves. This will indeed change the entire industry outlook for 2023 and beyond. It is quite appreciative how banks and fintechs are collaborating on the same forefront as allies.
Summary
- Introduction: Banks Can Play the Fintech Game Too
- Public confidence In New Tech?
- Prepare For 2024!
- Fintech’s Expanding Universe: Breaking Boundaries Beyond the Banking Industry
- Quantifying the Trends
- Fintech offerings in the Banking space
- 10 Best Digital Banking Institutions Of 2023
- Snippet from Global Fintech Interview series
- Conclusion
Introduction: Banks Can Play the Fintech Game Too
48% of people do not trust their bank to help them manage their finances during a recession, so how can these banking institutions and open-banking platforms expect to garner trust when engagement is clearly not there? Open banking indeed has revolutionized the way financial institutions interact with their clients evolving at an incredible pace.
Several traditional institutions have increased their investments in comparable goods as a result of this transition to a digital-first approach. For instance, in an effort to penetrate the fintech market, investment bank Goldman Sachs created the consumer lending platform Marcus in 2016.
Yet, many computer-savvy business observers caution that keeping up with developments spurred by fintech involves more than just more IT spending. Fintech firms and traditional banks are utilizing new technology to reimagine banking in a digital environment. Competing with lighter-on-their-feet startups needs a considerable change in thinking, processes, decision-making, and even the organizational structure. They put a strong emphasis on smooth delivery, quickness, customization, and customer service.
“People need banking, not banks.” – Ranjit Sarai, President’s Choice Financial
Fintech businesses concentrate on streamlining intricate financial procedures to increase user accessibility. Consumers adore the quick responses, ease of use, and variety of communication channels provided by fintech businesses. Fintech businesses may improve their services and make them more appealing to clients thanks to new technologies and marketing techniques.
Also, fintech businesses can connect with customers who might not have access to conventional financial services or a bank account. The majority of millennials use mobile wallets from non-banking financial organizations and prefer to do their banking online. Peer-to-peer lending is also widely used by millennials, which has raised the fintech sector’s profile.
Read the latest article: 10 Best Applications Of AI In Banking
Public confidence In New Tech?
In 2022 ‘Banking Disruption Index’, was launched which is a quarterly assessment of customers attitudes toward their bank’s digital know-how. This index will help understand whether consumer sentiment towards digital banking is evolving at the same pace as innovation is taking place and whether banks – traditional and challengers need to reassess their digital offers.
As we moved into 2023, clients and banking institutions are battling a cost of living crisis which has impacted confidence irrespectively. This impact on financial confidence will have long-term consequences if action isn’t taken to help strengthen the belief that corporations and consumers have about their money, and how best to manage it. This is where the value of open banking financial transparency joins us.
63% of them have set up accelerators or startup venture funds. US banks alone have invested a staggering $3.6 billion in 56 different fintech startups. Conversely, only 7% of banks have done the hardest job of setting up their own fintech R&D offshoot to create proprietary solutions.
Read latest article: The New Wave: Decentralized Finance
Prepare For 2024!
The conditions are favorable for 2023 to be another prosperous year for open banking.
Positive sentiment surrounds the implementation of more prominent innovations in banking and financial control. As emergencies and economic downturns continue into the new year, banks, applications, and open banking platforms have a fantastic opportunity to demonstrate the value of their products during times of extreme importance.
Through open banking in 2023, consumers will be able to increase transparency around their finances, improve their financial literacy, and not have to sacrifice anything in terms of security, with full transparency on where and how their transaction and account information is being used, all while enhancing customer service.
Fintech’s Expanding Universe: Breaking Boundaries Beyond the Banking Industry
A lot has been covered under the FinTech RADAR 2023 which nutshelled the boosters of the fintech domain. Fintech organizations, which include startups, technology firms, and existing financial institutions, use emerging technologies like big data, artificial intelligence, blockchain, and cloud computing to make financial services more accessible and effective. Since the Internet and smartphone revolutions, financial technology has shifted to Web 3.0 and metaverse and become more unpredictable.
Transferring money, depositing a check with a smartphone, applying for credit without visiting a bank branch, acquiring capital for a business, and maintaining investments are a few further instances of financial transactions that can be completed without the assistance of a person. According to EY’s 2017 Fintech Adoption Index, one-third of consumers utilize at least two or more fintech services, and their awareness of fintech’s role in their daily lives is growing.
No. While banks and startups have developed practical fintech tools for everyday banking (such as bank transfers, credit/debit cards, and loans), many other fintech fields that focus more on personal finance, investing, or payments (among others) have become increasingly popular.
Quantifying the Trends:
- In the fight to attract and keep users, 81% of respondents said that customer trust in a brand is surpassed by quality of service.
- Fintech startups, according to 79% of participants, have the most appealing branding.
- Fintechs are seen by 59% of people as a global rival to banks that can displace more conventional methods of delivering financial services.
- As a result of the need to quickly improve the business model in order to compete with fintechs, 46% of respondents regard them as a significant danger.
- According to 71% of poll respondents, banks fall short of fintechs in terms of service delivery speed, ease of use, and simplicity.
- Fintechs will run banks, according to 30% of respondents, while 31% think traditional financial institutions will gain from fintech.
Read More: How Does Visa Generate Money From International Transactions?
Fintech offerings in the Banking space
- E-wallets
One of the most popular fintech solutions in the banking sector is the e-wallet. E-wallets have expanded significantly, which is a sign that FinTech services are on the rise. According to the Worldpay Report, e-wallets will continue to be a popular payment option for international e-commerce customers, accounting for 44.5% of all transactions by 2020, a rise of 6.5% from 2019.
Digital wallets are anticipated to account for 51.7% of all e-commerce payments by 2024. While some of the most well-known e-wallet firms in the world include Samsung Pay, PayPal, and Apple Pay, digital wallets are used for a wide range of transactions, including P2P payments, overseas remittances, utility bill payments, top-ups, ticket booking, and many other things.
There are also other independent wallets available, such as Starbucks Pay and Walmart Pay. Due to their alluring promotions, generous cashback, reward points, and other incentives, e-wallets have drawn consumers. Since users must connect their bank account information to the wallet in order to add money to it, e-wallets have a favorable impact on the banking sector by serving as the main source of digital payments.
E-wallets have also increased the number of customers using digital payment methods, which ultimately helps the banks. Additionally, due to E-wallets’ enormous success, many banks now understand their significance and see them as a cooperative way to embrace technological changes.
- Technology Using Smart Chips
The Thales Group estimates that there will be 10.81 billion EMV cards worldwide by the year 2020. A type of chip-based payment system known as smart chip technology sometimes referred to as EMV (Europay, Mastercard, Visa) technology, employs microprocessor chips to safeguard financial transactions. These chips, which are present in debit and credit cards, are made to make it more challenging for transactions to be fraudulent. The increased security of payment transactions is one of the most obvious effects of smart chip technology on the banking sector.
It is challenging for fraudsters to exploit stolen card information to make unauthorized purchases because these chips generate distinct codes for every transaction. As a result, card fraud has significantly decreased, and customer confidence in electronic payments has improved. Smart chip technology has also made it simpler for banks to adhere to Payment Card Industry (PCI) security regulations, which mandate that institutions take precautions to safeguard cardholder data. As a result, there are now fewer data breaches and lower expenses for banks.
- Biological Sensors
Biometric sensors are one of the many developments that the banking sector’s use of fintech has spawned. The majority of the top fintech trends and predictions make reference to this development. Iris scanners and biometric sensors are two examples of recent technological breakthroughs in ATMs.
By 2025, up to 20.6 million biometric sensor cards are anticipated to be in use, according to ABI Research. These innovations are ground-breaking because they do away with the need to carry a plastic card and know PINs. The customers benefit from incredible ease and convenience from this.
Since the customer may access their account without a password, these improvements not only make ATMs more user-friendly and convenient but also safer than before. The biometric ATMs identify the account owner via integrated mobile applications, fingerprint scanners, palm scans, and eye recognition. ATMs also use micro-veins for more precise and secure identification, which reduces the mistakes that ATMs make while identifying customers.
All of the clients who fear at the notion of losing their ATM card breathe a tremendous sigh of relief thanks to the biometric technology. Even if their card is lost, they may still access their money thanks to biometrics. Therefore, biometric technology has a big impact on the financial industry.
- Cellular Banking
Banks have been forced to develop mobile applications that provide convenient FinTech banking services as a result of the rise in smartphone usage. The use of these programs is referred to as mobile banking. The global market for mobile banking is anticipated to reach about US$1824.7 million by 2026, according to a study by Allied Market Research. Nowadays, the majority of banks offer a mobile banking application that offers nearly all of the services offered by conventional banks and has an intuitive user experience.
“The challenge for banks isn’t becoming digital, it’s providing value that is perceived to be in line with the cost or better yet, providing value that consumers are comfortable paying for.” – Ron Shevlin
They have also given customers the option of fingerprint recognition. Without using any hardware or software for biometric identification, the program handles this task. A mobile banking app allows users to execute a variety of banking tasks, including rapid bill payments, cheque deposits, account balance checks, statement requests, and many more.
- Synthetic intelligence
- Service chatbots using AI
FinTech companies have also developed AI-based customer care chatbots, which have recently gained popularity. By the end of 2022, cost reductions from chatbot service interactions are anticipated to total almost $8 billion, according to a Juniper Research report.
Chatbots are simply computer programs that simulate human conversation in text or voice using machine learning and natural language processing. Chatbots can be used to provide quick and effective customer service, answering frequently requested queries and assisting with straightforward tasks like checking account balances and paying bills.
The simultaneous handling of a large number of client questions by chatbots frees up human personnel to concentrate on more difficult jobs. Additionally, it can offer personalized advice and assistance, improving the client experience. Because they lower costs, increase customer satisfaction, and free up call center operators to add value, chatbots have thus become a crucial asset for all banks.
- Robotic Process Automation
It is an artificial intelligence technology that focuses on automating specific repetitive tasks. RPA helps to process financial information such as accounts payable and receivable more efficiently than the manual process and often more accurately.
- An increase in smartphone usage
According to a study, there will be 7.26 billion smartphone users worldwide by 2022. This number alone can be used to infer that smartphone use has significantly increased in the current era. Therefore, each of these users represents a prospective client for fintech and banks. Due to operating expenses, banks could not reach every locality. Here is where fintech aids banks in expanding their customer base.
- The majority of services are accessible online.
Nowadays, anything and everything can be purchased online. Everything can be found and purchased online, whether it be goods like food and prescriptions or services like cleaning and grooming. The user can utilize the funds in the bank to make online payments for services offered on the fintech app, such as ticket booking, bill payments, EMIs, and many more, by connecting fintech’s payment solutions with their individual bank accounts.
“We’re witnessing the creative destruction of financial services, rearranging itself around the consumer. Who does this in the most relevant, exciting way using data and digital wins!” – Arvind Sankaran
- Electronic payments
Digital payments refer to transactions that are speedy, secure, and cashless. Digital payments are facilitated by fintech apps with online payment systems, e-wallets, and digital currencies. One of the most well-known subsectors of the fintech sector tends to be digital payments. By 2021, the value of worldwide digital payments is predicted by Statista to be USD 6,685,102 Million.
- Online Banking
Banks create fintech apps for their customers because digital banking has evolved into a very practical means for both consumers and bank staff to manage client data. Fintech apps for digital banking enable customers to manage their bank accounts online without having to visit a bank for every little difficulty.
- Online Lending
Loan apps and lending software are examples of digital lending fintech applications that help lenders and borrowers communicate and settle disputes. Fintech apps are used by financial institutions like banks and private lenders to streamline and effectively manage loan processes.
- Internet investment
Investors can analyze and invest in a variety of financial assets and stock markets using digital fintech investment apps. These apps serve as a platform to enable investing and provide users with pertinent and informative data they can use to make educated decisions about their investment plans.
- Consumer lending
Fintech apps for consumer finance assist their users in managing their own finances. Users of these apps are given the tools and capabilities they need to effectively manage their spending, create budgets, and engage in deliberate spending.
- Increase competitiveness
Banks are able to maintain their competitiveness in the digital sphere thanks to fintech solutions. By using these technologies, banks may boost productivity, cut expenses, and enhance client experiences. Additionally, fintech firms give banks access to cutting-edge technologies that help them learn crucial information about their customers and improve their goods and services.
Read: Let’s Dive Deep Into Fintech Vs The Conventional Banking
10 Best Digital Banking Institutions Of 2023
As neo and challenger banks disrupt traditional global incumbents, we rate the leaders from a stodgy, slow-moving space to one that’s innovative and dynamic. Almost all digital banks provide low-cost services which are delivered fast than those offered by their incumbent counterparts. So, let’s take a look at the global top 10 digital banks
This Australia-based Judo Bank was founded in 2018 and already serves over 10,000 customers, making it one of Australia’s most recent unicorn fintechs. It serves both business and individual customers. In 2020, it raised $ 216 million in seed funding, and in 2021, it was valued at $ 2.6 billion. This is a certain 100 percent mind-boggling increase in JudoBank’s 2019 market value.
Since its founding in 2013 by technology experts, MoneyLion has been a rising star in the banking industry. Initially, it provided financial services, but it has since expanded to investment and lending products. This fintech expanded into the realm of digital banking. MoneyLion partnered with Fusion Acquisition Corp to launch its IPO in 2021, resulting in a combined equity valuation of $ 2.9 billion.
Monzo, a London-based banking upstart valued at $1.6 billion, was founded in 2015 and currently serves 5 million customers in the UK and US. In 2016, its digital banking appraised over $1 million on Crowdcube, setting a new record. Blomfield resigned as CEO in May of 2020.
Starling Bank, founded in 2014 in London by banking veteran Anne Boden, is a digital challenger that specializes in business current accounts. It raised $152.5 million in 2022, with a pre-money valuation of approximately $2.9 billion. Starling Bank currently serves 2,7 million customers, and its revenue increased by a staggering 600% in the previous fiscal year.
- N26
This bank, which was founded in 2013 and is headquartered in Germany, is led by young entrepreneurs. It has seven million or more customers in 24 countries. Currently, it is one of Europe’s most impressive neobanks. N26 has left the UK market, citing Brexit, and is now solely focused on the European market. The closest competitors to N26 are Revolut and Monzo.
SoFi, an acronym for ‘Social Finance,’ was founded in 2011 in San Francisco with a US$ 2 million loan to connect newly-graduated Stanford students with alumni. Mike Cagney, James Finnigan, Ian Brady, and Dan Mackenzie were the founders. SoFi acquired full-service national bank status by October 2020 and is now valued at $5.26 billion. Despite this, pre-IPO estimates suggested that SoFi would be worth nearly $9 billion by 2021.
Chime operates primarily in San Francisco and is currently valued at $14.5 billion. It specializes in retail banking and serves approximately 12 million customers, making it the most valuable retail-serving fintech startup in the United States. During the pandemic, the bank’s clients’ increased reliance on digital channels resulted in an unexpected growth of nearly 50 percent.
Tinkoff was founded in 2006 in Moscow and is renowned for having the longest-established digital banks. It currently has approximately thirteen million customers. Tinkoff is estimated to be worth US$17 billion based on data from its London Stock Exchange (LSE) listing, and it has just revealed that its total assets are worth RUS1.318 billion, a figure that has increased by an astounding 50% annually. Despite the difficulties of recent months, Tinkoff’s total assets have increased annually since 2018.
Revolut, a London-based company founded in 2015, took the European banking industry by storm. It was recently valued at approximately US$ 33 billion. It also partnered with fintech titan Stripe as a strategic move to provide the business hub with a broader range of products. Revolut left Canada in 2021, citing difficulties in obtaining a license to operate as a full bank within Canada’s financial sector. The move followed the 18-month-old successful launch of Revolut’s beta version in Canada.
Nubank became the most successful digital bank to date after launching in 2013 as a direct response to Brazil’s overcharging, undeserving incumbent banks. It reflects a desire to create something completely new and reflects the streamlined nature of Nubank’s products. This challenger bank currently serves an estimated 70 million customers, with a predicted valuation of US$ 126 billion by 2025 based on current growth forecasts. The NPS score of +87 for Nubank is just one indicator of its popularity among customers.
Read: A Global Map Of Cryptocurrency Regulations
Snippet from Global Fintech Interview Series
Michael Hagedorn, Senior Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer at Valley National Bank shares more on the future of banking and the impact of fintech in the B2B marketplace in this chat with GlobalFinTechSeries.
- There are a few clear trends emerging that help shape what it might look like and what financial providers will need to do to remain relevant in the customer’s eye. First, digital technology will allow the customer to conduct business when and how they want. It will be device agnostic and transactions that today require human interaction will be completed by the customer without upfront human assistance. Second, digital technology will impact all lines of business within a traditional bank, including commercial banking. And finally, the manner in which customers are defined will change. Loyalty will need to be real and customer acquisition will not be solely based upon price and/or product features, but more importantly how easily someone can do business with your bank and how your firm can demonstrate that they are furthering society of key areas important to customers.
- Reorganizing processes alone is not enough to drive better outcomes. The integration of intelligent solutions into banking operations, like AI and machine learning, are driving innovation in the banking industry. More often than not, meaningful business decisions are only as good as the data used to inform them, and the leading banks are using AI to distill massive amounts of data into actional insights.
Conclusion
Making a choice between fintech and traditional banking is challenging because both of these systems have important benefits, as this blog has shown. Yet as the environment evolves and improves constantly and new technologies are introduced to the market, fintech has become the most popular choice. As a result of using technical trends and breakthroughs, it has a wider market distribution.
Banks, on the other hand, are financial institutions that are authorized to lend money and take deposits from their clients. They concentrate on security and the control of financial risks, which limits their market reach. Yet, with fintech, users have access to a number of cutting-edge features as well as the same services as traditional banks. And if consumers don’t entirely migrate from banks to fintech, this makes the connection between banks and fintech companies quite straightforward and comfortable. But, if banks and organizations in the fintech sector can work together, they will have a significant impact. Banks have been able to boost productivity, cut expenses, and enhance customer experiences thanks to fintech technologies. Additionally, banks use fintech tools like Blockchain and Artificial Intelligence to offer their clients more individualized and secure services.
Banking has been revolutionized by fintech solutions, which have increased efficiency, decreased costs, bolstered security, enriched the customer experience, broadened access, sped up payments, and more. Financial institutions can’t survive in today’s digital market without adopting these innovations. To survive and grow in today’s dynamic market, banks must make significant investments in fintech solutions and adopt digital strategies.
This blog has shown that comparing fintech to traditional banking is challenging because both have their benefits. But, as the world continues to change and develop, and as new technologies emerge, fintech has emerged as the most viable solution.
[To share your insights with us, please write to sghosh@martechseries.com]