Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is reshaping the finance industry by offering services traditionally managed by banks, insurance companies, and brokerage firms through blockchain technology. DeFi enables users to borrow, lend, earn interest, trade assets, and more—without relying on intermediaries such as banks or financial institutions. This decentralized model eliminates the need for a central authority, operating instead through smart contracts—self-executing agreements coded into the blockchain.
For many, DeFi represents a more efficient and transparent alternative to traditional financial infrastructures, which are often criticized for being outdated, opaque, or overly centralized. As DeFi continues to gain traction, questions arise about its long-term impact on the traditional banking system. This article explores the evolution of DeFi, its challenges, and the potential future for both decentralized and traditional financial systems.
What is Decentralized Finance (DeFi)?
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) refers to a suite of financial services built on blockchain networks such as Ethereum. Unlike traditional finance, which relies on centralized intermediaries like banks, DeFi leverages smart contracts—self-executing agreements with terms encoded in code. This enables peer-to-peer transactions, reducing costs and increasing efficiency by eliminating the need for third-party intermediaries.
Core Principles of Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
For a financial system to be classified as DeFi, it must adhere to certain foundational principles that ensure its decentralized nature and functionality.
1. Decentralization
DeFi eliminates the need for central authorities or intermediaries, such as banks or financial institutions. Instead, financial services are administered autonomously and transparently through blockchain technology, allowing users to directly control and manage their assets.
2. Accessibility
DeFi is open to anyone with a digital wallet and internet connection, removing barriers like traditional bank accounts or credit histories. This inclusivity makes DeFi accessible to a broader global audience.
3. Transparency
All transactions within DeFi systems are recorded publicly on the blockchain, ensuring transparency. This allows any participant to verify and audit transactions, fostering trust and enhancing the integrity of the system.
4. Interoperability
DeFi applications are built to work seamlessly with one another, creating an interconnected ecosystem of financial services. Users can easily interact with multiple platforms and services, enhancing the overall utility of the decentralized finance space.
5. Open Innovation
DeFi promotes open innovation, enabling anyone to develop new applications and protocols. This openness accelerates the evolution of DeFi, driving continuous innovation and diversification within the ecosystem.
Technologies Driving DeFi: Blockchain, Smart Contracts, and Cryptocurrencies
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is built upon three fundamental technologies: blockchain, smart contracts, and cryptocurrencies. These technologies provide the foundation for the global DeFi ecosystem, enabling financial inclusion and innovation.
Blockchain Technology
At the core of DeFi is blockchain, a decentralized ledger that records all transactions across a distributed network. Major blockchains like Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, and Solana serve as the infrastructure for DeFi applications, or dApps. While Ethereum remains a leader due to its mature ecosystem, rising transaction fees and network congestion have led to increasing interest in alternative blockchains that offer improved scalability and lower costs.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements where the terms are encoded in computer code. They automate financial processes without requiring intermediaries, ensuring trustless transactions. Smart contracts power DeFi protocols like Uniswap, Aave, and Compound, which provide decentralized trading, lending, and borrowing services.
Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies, particularly Bitcoin, are gaining traction in developing economies as a hedge against currency devaluation and as a tool for financial inclusion. Countries like Nigeria and El Salvador have seen significant adoption of Bitcoin, and platforms in India now facilitate direct Bitcoin-to-INR conversions, making DeFi more accessible globally.
Oracles
Oracles play a crucial role by providing smart contracts with external data needed for real-time decision-making. Platforms like Chainlink ensure DeFi protocols can access accurate information such as price changes or interest rates, ensuring the correct execution of smart contracts.
Read More : Global Fintech Series Interview with Jeff Marsden, Chief Product Officer at PureFacts
Key Players in the DeFi Space
1. AAVE
2. Uniswap
3. MakerDAO
4. Curve Finance
5. Lido Finance
Market Growth and Adoption Rates for DeFi
The global Decentralized Finance (DeFi) market was valued at approximately USD 22 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow to USD 48.02 billion by 2031, with a CAGR of 9.06% from 2024 to 2031. DeFi provides a broad range of financial services, making it a popular choice for brokerages, banks, and exchanges. Its applications allow users to borrow, lend, trade cryptocurrencies, and speculate on asset prices through derivatives. DeFi platforms also offer risk insurance and enable consumers to earn interest on their savings, contributing to the sector’s rapid growth.
Increased efficiency and the rise of DeFi tokens in gaming and e-sports have further driven adoption. Players use DeFi tokens to trade collectibles and build ecosystems in blockchain-based games, which has expanded the use of DeFi across various industries. Platforms like Augur allow users to trade on global events, including sports and economic trends, enhancing DeFi’s reach.
The future growth of DeFi is expected to benefit from blockchain-based prediction systems. DeFi removes the control financial institutions have over assets and eliminates service fees typically charged by banks. Its global accessibility, coupled with the ability to trade tokenized investments, positions DeFi as a major disruptor in the financial sector.
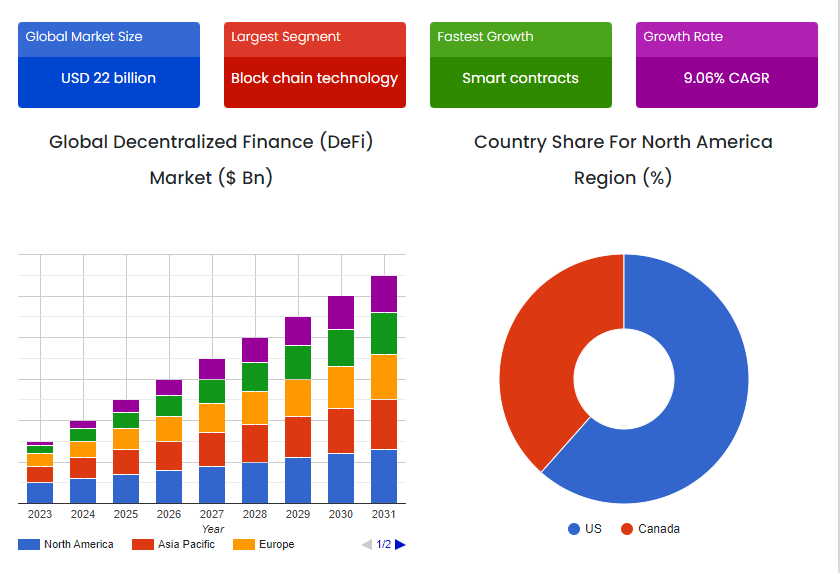
Source: SkyQuest
Key Differences Between DeFi and Traditional Banking
| Aspect | Traditional Banking | Decentralized Finance (DeFi) |
| Centralization vs. Decentralization | Centralized institutions like commercial and central banks act as intermediaries in transactions. Transactions require human intervention and can take days, especially for cross-border transfers. | DeFi operates on decentralized networks using blockchain technology. Transactions are carried out automatically via smart contracts without intermediaries, enabling near-instant transfers at lower costs. |
| Transparency | Most operations are opaque. Customers have limited access to information regarding loans, fees, and fund management. Banks control the flow of information. | Built on public blockchains, all transactions in DeFi are transparent and visible to anyone. Users can audit transactions, view liquidity pools, and monitor how funds are managed. |
| Accessibility | Geographical restrictions, credit checks, and minimum balances limit access to banking services. | DeFi is accessible to anyone with an internet connection, regardless of location or financial background. No credit checks or minimum balances are required. |
| Smart Contracts vs. Manual Processes | Traditional banking processes like loan approvals involve human intervention, paperwork, and manual checks, which can be time-consuming. | DeFi uses smart contracts to automate processes like loan issuance and collateral management. Smart contracts self-execute based on predefined conditions, eliminating the need for human intervention. |
| Trust Model | Operates on a trust-based system where customers rely on institutions to manage their assets and execute transactions properly. | DeFi is trustless, relying on cryptographic algorithms and transparent code. Users retain control of their assets without needing to trust a central authority. |
Synergies Between DeFi and Traditional Banking
Blockchain technology, once viewed as a disruptor to traditional banking, is now gaining traction within financial institutions. Leading banks are increasingly adopting blockchain to modernize their services. JPMorgan’s Quorum, an enterprise blockchain solution, exemplifies how traditional banks can enhance transaction speed and transparency while maintaining regulatory compliance. By implementing blockchain, banks can streamline operations and offer more efficient services without compromising on oversight.
DeFi is not necessarily a replacement for traditional banking; rather, it presents opportunities for collaboration. Financial institutions are exploring partnerships with decentralized finance platforms to provide hybrid services. For instance, banks can collaborate with DeFi lending protocols to extend loans within regulated frameworks, offering the security of traditional banking with the flexibility of decentralized finance.
Furthermore, the tokenization of real-world assets is creating new possibilities for banks. By tokenizing assets like real estate, banks can enable fractional ownership, enhancing liquidity and democratizing access to investment opportunities. This innovation allows traditional banks to remain competitive in an evolving financial landscape, providing customers with cutting-edge investment options alongside conventional services.
Challenges and Risks Surrounding DeFi
Security Vulnerabilities
DeFi platforms face significant security concerns due to the immature nature of the technology behind them. Built on complex smart contracts, these platforms are vulnerable to hacks and exploits, as demonstrated by several high-profile incidents in the market.
Regulatory Uncertainty
The DeFi sector operates largely without regulation, which introduces risks such as fraud, scams, and financial mismanagement. The absence of clear legal oversight complicates tax collection and anti-money laundering efforts for both users and regulators, leaving a gap in accountability.
Lack of Consumer Protection
Unlike traditional financial systems, DeFi lacks established consumer protection mechanisms. Users are responsible for securing their wallets via private keys. If a private key is lost or stolen, access to funds is permanently lost, as most DeFi platforms do not offer key recovery systems. Global transactions in DeFi also make it difficult to recover funds in the event of an error or fraudulent activity.
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities
Many DeFi issues stem from weaknesses in smart contract code. Even a minor flaw can lead to significant financial losses for users. The decentralized nature of DeFi magnifies the impact of these vulnerabilities.
Navigating Complexities and Scams
The rapidly expanding DeFi landscape presents challenges for investors, who must distinguish between legitimate opportunities and fraudulent schemes. The increasing number of scam projects makes navigating DeFi more complicated and risky for newcomers.
Market Volatility
External factors like geopolitical conflict, inflation, and regulatory concerns heavily influence the DeFi and cryptocurrency markets. As a result, both markets experience high volatility, making them riskier for investors.
Collateralization Constraints
In DeFi’s crypto lending sector, borrowing is often limited by collateral value. DeFi protocols can liquidate collateral without notice in the event of default, adding another layer of risk for borrowers.
Scalability and Liquidity Issues
DeFi platforms currently struggle with low scalability, leading to high transaction fees and slower processing times. Additionally, new platforms often face liquidity challenges, with too few accounts or collateral assets to attract widespread participation.
Strengthening DeFi: Addressing Risks and Expanding Potential
While DeFi offers immense opportunities, it also demands careful attention and responsibility from users. The decentralized nature of DeFi places the burden of security on the individual, but developers must continuously working to improve safety measures. As the DeFi sector evolves, new solutions are emerging to tackle existing risks and enhance the user experience.
What’s Next for Traditional Banks?
As DeFi continues to grow, traditional banks are finding opportunities to integrate blockchain technology into their services. Blockchain offers enhanced transparency, efficiency, and cost reduction, exemplified by initiatives like JPMorgan’s Quorum. By adopting aspects of decentralized finance, banks can modernize their offerings to remain competitive.
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) present another opportunity for banks to bridge the gap with DeFi. As stable, government-backed digital assets, CBDCs combine decentralization benefits with the trust and security of traditional banking systems, offering a new model for digital transactions.
Banks can also leverage stablecoins such as USDC or DAI to facilitate faster, more efficient cross-border payments and settlements. These digital assets provide price stability while operating on decentralized networks, helping banks streamline remittances and enhance transaction speed.
By improving a hybrid approach that combines the efficiency of DeFi services with the regulation and compliance of traditional banking, financial institutions can adapt to the evolving financial landscape.
Read More : AI Can Save E-commerce Vendors from Cash Flow Squeeze
[To share your insights with us, please write to psen@itechseries.com ]
