Social media and trade journals may seem to be awash in trends, but it takes time to sift through everything to find the ones that matter. This blog shall enlighten the KYC market, its data, and new tech of eKYC and digital solutions thereby in the decentralized market scenario.
KYC has been harnessing technology to disrupt and democratize the banking space. Let’s see how?
Summary
- Introduction
- KYC: A Comprehensive Overview of Its Characteristics
- Fintech exclusive: Industry Viewpoint from 2 leaders
- Exploring the Different Types of KYC: A Comprehensive Guide
- Uncovering the Growing Vitality of KYC
- Legal Implications of KYC: What You Need to Know
- Top Podcasts for Regulatory Compliance & KYC in 2023
- Centralized vs Decentralized Providers
Introduction
Know Your Customer (KYC) can also refer to Know Your Client. While opening an account and on a regular basis after that, the client’s identity must be identified and verified through a process called KYC, or KYC check. In other words, banks need to confirm that their customers are actually who they say they are.
The Know Your Client (KYC) rule is an industry-wide code of conduct for anyone opening or servicing a client’s securities account. It is implemented at the outset of the customer-broker relationship to build the essential individual profile of each client before any financial advice is given. It is also made plain to the client that they must comply with all applicable laws, rules, and industry standards when dealing with securities.
KYC: A Comprehensive Overview of Its Characteristics
There is persistent discussion among blockchain enthusiasts about whether or not KYC solutions are necessary for distributed networks. Regulation, privacy, and Decentralisation all have a role in shaping the perspectives of various parties.
- Quartz is a solution by Tata Consultancy Services that utilizes blockchain and AI technology to meet the Know Your Customer, Anti-Money Laundering, and Fraud management requirements of financial institutions.
- Wipro’s answer, Dice ID, is a distributed system for checking user IDs and passwords.
KYC Should be:
- Can assist platforms in reducing legal risks and showing compliance.
- Can lessen the chances of fraud, identity theft, and other forms of fraud occurring in decentralized systems.
- May verify the identity of users, a key step in building trust between them.
KYC Should not be:
- By requiring the gathering and storage of personally identifiable information that may be vulnerable to breaches or abuse, KYC rules go counter to these values.
- Those without proper identification or who reside in areas with restricted access to conventional financial services may find KYC procedures to be an impediment.
- There is a risk that integrating KYC solutions may increase the platform’s complexity and undermine its decentralized character.
Read More links for Fintech – FinTech RADAR: 105 U.S. Fintech Unicorns And Their Core Offerings
For me, the use cases, regulatory environment, and ultimate objectives of platform operators determine whether or not KYC solutions are necessary on decentralized platforms. For decentralized systems to thrive and be widely adopted, they must find a happy medium between regulatory compliance, privacy, security, and inclusion.
Read: 5 Unconventional Ways To Make Money On Crypto In 2023
Industry Viewpoint
 We had a one-on-one discussion briefly with a renowned market leader Timothy Rooney, President, Marygold & Co. Below is his exclusive view in regard to decentralized KYC which has been given to the Global fintech series.
We had a one-on-one discussion briefly with a renowned market leader Timothy Rooney, President, Marygold & Co. Below is his exclusive view in regard to decentralized KYC which has been given to the Global fintech series.
 Decentralized KYC systems are pivotal in maintaining integrity and trust in the finance and business world. These systems leverage blockchain-like technology to verify identities, departing from traditional centralized methods. KYC processes are essential, especially in high-risk sectors like fintech, gambling, and crypto. Decentralized KYC can ensure secure and trustworthy transactions, offering benefits such as enhanced fraud prevention, trust building, and regulatory compliance. Their impact extends beyond finance, benefiting government, healthcare, education, and enterprise sectors.
Decentralized KYC systems are pivotal in maintaining integrity and trust in the finance and business world. These systems leverage blockchain-like technology to verify identities, departing from traditional centralized methods. KYC processes are essential, especially in high-risk sectors like fintech, gambling, and crypto. Decentralized KYC can ensure secure and trustworthy transactions, offering benefits such as enhanced fraud prevention, trust building, and regulatory compliance. Their impact extends beyond finance, benefiting government, healthcare, education, and enterprise sectors. Exploring the Different Types of KYC: A Comprehensive Guide
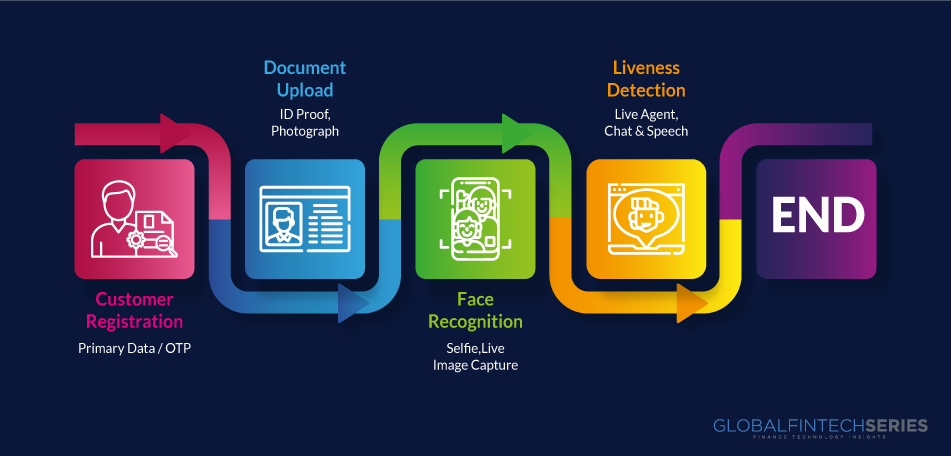
It is crucial for organizations and people to have a firm grasp on the various Know Your Customer (KYC) processes available to them. You may learn about the five different kinds of Know Your Customer procedures in this post in less than five minutes. After finishing this short read, you’ll have a firm grasp on the several Know Your Customer (KYC) approaches, their advantages, and the ways in which they may safeguard your personal information.
Traditional KYC
The classic Know Your Customer procedure is up first. Collecting fundamental information like name, address, and date of birth is the standard method used to identify customers. Customers must also provide identification and an address verification document such as a passport, driver’s license, or recent bill. Although many banks and other financial institutions use traditional KYC, it may be a tedious and invasive process for clients.
Electronic KYC or eKYC
Next, we have eKYC, or electronic Know Your Customer, which streamlines the traditional KYC procedure via the use of technology. Customers may now complete their Know Your Customer requirements online, using a secure portal or mobile app, saving them time and effort. Electronic Know-Your-Customer (eKYC) processes authenticate a customer’s identification using cutting-edge tools including digital signatures and biometric verification. The speed and simplicity of this KYC method have led to its widespread acceptance in a number of different sectors.
Read: Global Fintech Interview with Jitin Bhasin, Founder & CEO at SaveIN
Simplified KYC
Simplified Know Your Customer (KYC) is the third kind of KYC, and it requires less paperwork and is aimed at low-risk clients. People who don’t have pressing needs for a wide variety of goods and services would benefit greatly from this. Customers and companies benefit from a less onerous onboarding process when KYC requirements are simplified. It’s best for consumers with minimal credit risks, so it may not work for everyone.
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD)
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) is our fourth kind of Know Your Customer check, and it’s obligatory for high-risk customers or transactions. With EDD, a deeper look into a client’s history and finances is conducted. It might include looking into the customer’s political connections or criminal history, as well as validating the legitimacy of their money and knowledge of their company. Even though EDD is a more involved KYC procedure, it is necessary to reduce the dangers connected with high-risk clients.
Decentralized One-Click KYC
Decentralized know-your-customer (KYC) solutions provide a novel method of establishing client identity while protecting sensitive information. Toggle is an example of a decentralized KYC solution that puts control of a user’s data back in their hands. Users may share their information with companies using Toggle while still maintaining full control over their personal information. Unlike conventional KYC techniques, this cutting-edge variant places a premium on the privacy and security of its users’ data.
Uncovering the Growing Vitality of KYC
Observance of the RulesIn 2023, compliance with local and international regulations is a primary reason why KYC is necessary and essential. Strict anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorism funding (CTF) legislation have been enacted by governments around the world to thwart illicit activity. These rules ensure that financial institutions don’t unwittingly aid criminals by requiring extensive customer identification and verification procedures.
Generate AI Images From Text Using DALL-E : A Revolutionary Tool By OpenAI
- Prevention of Financial Crimes– KYC plays a crucial role in preventing financial crimes such as money laundering, terrorist financing, and fraud. By verifying the identity of customers and monitoring their transactions, businesses can detect and report suspicious activities. This helps authorities identify and apprehend criminals, protecting the integrity of the global financial system.
- Building Trust with Customers– In an increasingly digital world, trust is more important than ever. By implementing robust KYC measures, businesses demonstrate their commitment to protecting customers and combating financial crime.
- Facilitating Global Business Operations– In today’s interconnected world, businesses must comply with various regulations across different jurisdictions. This enables them to expand their operations globally and tap into new markets with ease.
- Risk Management- Implementing a comprehensive KYC process allows businesses to manage risk more effectively. The best way for businesses to identify hazards and take precautions is to learn as much as they can about their customers’ histories and buying habits. This helps companies shield their assets, good name, and clientele from harm.
Legal Implications of KYC: What You Need to Know
International and Domestic Regulations
Failure to execute KYC requirements may have far-reaching legal consequences. Large monetary penalties, regulatory punishments, and even criminal prosecution are all possible outcomes for businesses. As more and more local and international laws have been enacted to combat financial crime, the regulatory climate has hardened. Regulations like this may be found in places like the United States Bank Secrecy Act (BSA), the European Union’s Fourth and Fifth Anti-Money Laundering Directives (4AMLD and 5AMLD), and the Financial Action Task Force (FATF).
Understanding Legal Implications of No KYC
Failure to execute Know Your Customer (KYC) practices may result in penalties, such as monetary fines. Companies that fail to meet regulatory standards may be subject to severe financial fines. In 2020, for instance, a large international bank was fined $400 million by the US Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC) for failing to build an efficient risk management framework and for failing to comply with KYC standards. In a separate incident from 2018, a European bank was fined €775 million for failing to adequately implement AML and KYC procedures.
Companies may risk regulatory repercussions, such as fines if they do not have proper know-your-customer (KYC) systems in place. License revocation or suspension, operational limits, and enhanced oversight from authorities are all examples of possible punishments. In addition, businesses that don’t follow KYC rules risk losing the respect of their clientele, business associates, and potential investors.
Companies that fail to execute KYC procedures may be subject to criminal prosecution as well as civil penalties and regulatory punishments. Employees and executives who are proven to be in violation of these policies may be held criminally accountable for their actions. In 2020, for instance, the CEO of a cryptocurrency exchange was arrested and faced charges of failing to comply with Know Your Customer and Anti-Money Laundering laws.
Top Podcasts for Regulatory Compliance & KYC in 2023
This podcast provides listeners with information on the fields that equip professionals to resist criminal activities that threaten people, companies, and society, with a focus on financial crime prevention. The podcast features in-depth discussions on identifying and reducing risks facing businesses and communities with writers, subject matter experts, and practitioners.
From GDPR 101 all the way through data subject access requests and GDPR compliance for online retailers, this podcast has you covered. You’ll have a better grasp of GDPR compliance and discover actionable tactics for attaining compliance by listening to this podcast.
If you work in regulatory compliance in Europe, you should check out the Compliance Matters podcast produced by the International Compliance Association, a professional membership organization for compliance professionals.
Legal & Compliance Insights Podcast
If you’re interested in keeping up with regulatory compliance in Europe, the Compliance Insights podcast from Thomson Reuters, a major supplier of news and information for companies and professionals, is a great place to start.
Keeping abreast of the most recent data privacy rules and best practices is essential for many European firms.
Centralized vs Decentralized Providers
Financial institutions and other businesses must follow the Know Your Customer (KYC) procedure to confirm the identification of their clients. Customer data from government-issued papers, financial records, and personal data must be gathered and stored as part of KYC procedures. The actions related to the clients’ verification are often carried out by companies mandated to undertake KYC via external KYC providers.
Read: Let’s Dive Deep Into Fintech Vs The Conventional Banking
After processing, KYC data is often kept in centralized databases that are owned and managed by the financial institution or the KYC provider. Depending on the specifics, the KYC provider and the financial institution may each keep the data differently, but this is the norm.
Customer data must be gathered, verified, and then stored on the servers of the KYC provider, such as a third-party verification service. While in some cases KYC providers just briefly keep the confirmed information, in others the storage is ongoing. In any situation, the organization that requested the verification receives access to the confirmed consumer data.
Additionally, the organization often keeps the KYC information in a centralized database since they need access to it for continuous risk and compliance monitoring.
In accordance with the applicable privacy and data protection laws, both the KYC provider and the organization are responsible for the keeping of personal information if they both keep a copy of the confirmed KYC data. The particular structure, including the responsibilities that will be played, will be determined by the agreements reached between the parties and any applicable legal or regulatory requirements.
Although relying on centralized storage, whether it be for the organization or the KYC provider, has the advantages of being simpler to administer and more secure, it also comes with a number of potential risks, such as the possibility of a single point of failure and vulnerability to data breaches.
The use of decentralized storage options for KYC data is becoming more popular for the reasons listed above, among others. Instead of using a single centralized server to store and handle data, decentralized storage uses dispersed networks of nodes. For KYC providers, this strategy may provide various advantages, including improved security, privacy, and resilience.
Conclusion
Businesses will confront a more complicated regulatory environment, changing technology, and increased client expectations in 2023, which will increase the demand for thorough KYC processes. Businesses may manage risk, adhere to laws, and build client trust by recognizing the significance of KYC and implementing a solid and dependable solution. For decentralized systems to thrive and be widely adopted, they must find a happy medium between regulatory compliance, privacy, security, and inclusion.They will be in a better position as a consequence to prosper in the digital age and overcome the difficulties that lie ahead.
Agreed, KYC has been harnessing technology to disrupt and democratize the banking space with all the above points put forth. But, how far its footprints shall work, is a question solved. May be we get a new technology which shall create a boom in the tech industry or is this decentralization is hyped and just a bubble which shall soon be replaced.
[To share your insights with us, please write to sghosh@martechseries.com]