The fintech domain has given us several proofs making us believe in the power of digital transformation to reach underserved and remote communities in the context of the healthcare sphere. With a combination of various offline services (hospital finance agents) and technology (e-wallets), fintech provides trusted formal financial services in the health industry to people who otherwise would be unable to access such services. Let’s have a closer look at the fintech and healthcare relationship.
Where Is Fintech For Health Already In Use?
The influence of Fintech on the Health industry is still nascent. Digital healthcare financial service models have emerged with strong donor backing and were built upon digital wallets framework (e.g. M-TIBA created by M-Pesa and PharmAccess). Fintech for Health has started to emerge as a central focus in Asia for healthcare companies and digital health startups which focuses itself on low- and moderate-income audiences. Fintech startups that are in the growth stage, with outbound investment profiles are rapidly trying to move into new domains like healthcare.
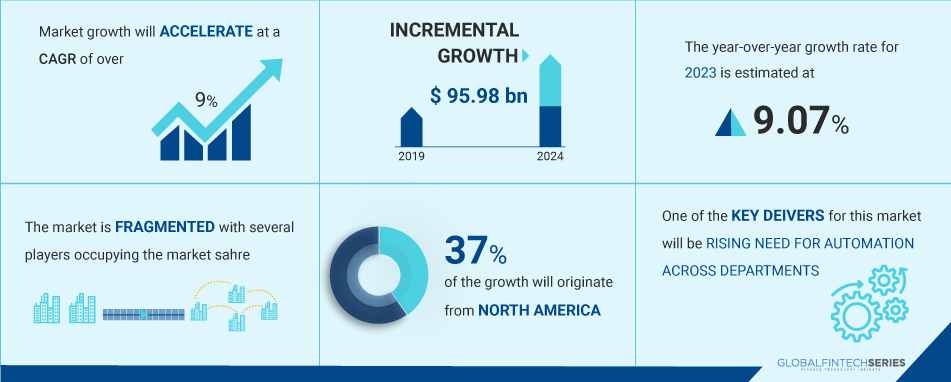
Below is the graphical representation of the digital healthcare market where we can see the acceleration of CAGR at 9% and fast incremental growth from 2019 to 2024 i.e. $96 billion approximately. The market seems quite fragmented with many players fighting for their share of the market. One of the key drivers for this market will be the rising need for automation across departments with 37% of the growth coming from the North American market as the highest figure in the tail.
Read: 9 Best Fintech Innovations Of 2022
Healthcare Payment And Access Challenges
Above we have discussed all the positive aspects of healthcare and fintech; now let’s limelight a few of its challenges and payment hazards. All through the journey of any patient, from prevention to palliative care, there is an accompanying financing journey. Despite governments’ re-commitments to the goals of universal health coverage (UHC), a major cost element of healthcare is borne by the patient itself, especially for high-quality care that is delivered timely. In healthcare, costs are expensive, mostly paid out of pocket, entailing high transaction costs, and not linked to health outcomes as expected. Such costs prohibit people from accessing the apt care, at the apt time, and at the apt place. The financing journey includes high care costs for shorter time frames (like advanced diagnostics, chemotherapy, surgery), low care costs over a long period of time (like chronic disease management, loss of caregiver income), or preventive care for which the return on investment may not be immediately clear to patients. This in turn takes the shape of financial pain thereby impacting both care access and financial health after seeking care. When care is unaffordable, patients either forgo care or they try to find some other alternative solutions to fund them, including borrowing or selling assets.
Here’s How Healthcare Systems Are Improving With Fintech:
1) Making healthcare more cheap – Up-and-coming firms are reshaping the relationships between patients, payors, and providers by utilising the fintech playbook to solve healthcare issues. More than 65% of people worldwide lack insurance, including those covered by public and commercial programmes. Government programmes support the remaining 35% of the population, and private health insurance policies exclude outpatient care and other medical expenses from their coverage.
2) Making health insurance more accessible to people with middle-class to low-income levels – Health insurance remains the main source of funding for medical care. Government programmes are continuously being run to promote insurance penetration, raise awareness of the issue, and provide coverage for the world’s uninsured population.
3) Increasing data accuracy with blockchain – Blockchain technology, a type of fintech, enhances data efficiency in the healthcare industry. With the use of modern technology, healthcare institutions may now save and exchange patient data via hospitals, diagnostic laboratories, pharmacy companies, and clinicians. It can easily spot serious errors, eliminate the worry about data manipulation in healthcare, and support the special data storage patterns at the highest level of security.
4) Expanding the scope of telemedicine – New technologies are lightening the load on hospitals by enabling online doctor consultations in real-time. Telemedicine reduces wait times for appointments and raises the standard of care in remote locations. In 2023, it’s possible that $350 billion of US healthcare spending will be transferred to virtual or virtually enabled treatment.
The health technology, pharmaceutical, and insurance industries are watching with bated breath since Amazon announced its partnership with Warren Buffet’s Berkshire Hathaway and with JP Morgan. (Amazon and Warren Buffet usually get the most attention in the partnership, but JP Morgan’s potential role should not be underestimated). In China, when Jack Ma broadened Alibaba’s focus to healthcare, the rest of Asia paid attention.
Read: 10 Tech Trends In 2023 You Must Be Ready For
[To share your insights with us, please write to sghosh@martechseries.com]
