PayFac Model: Introduction
The payfac model was developed to enable payment-specific organizations to streamline the process of getting started with online payments, provide services to a wider range of businesses, and concentrate on their core competencies.
What Does a PayFacs Do?
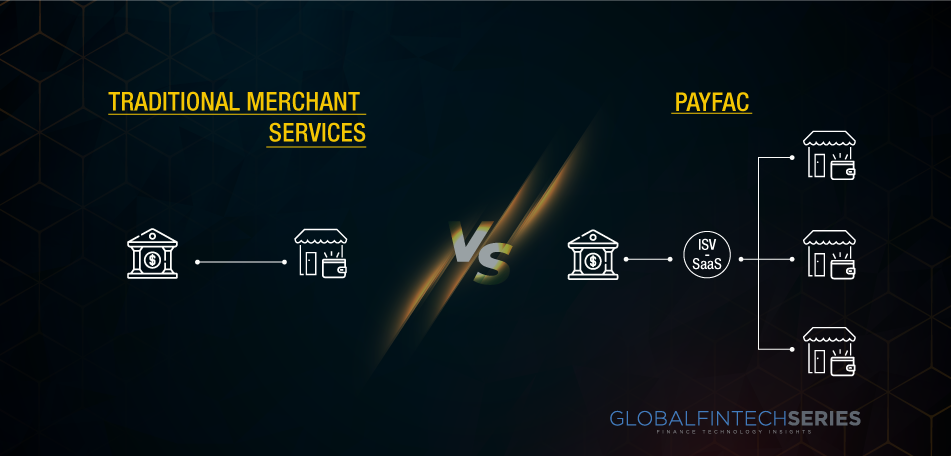
When a PayFac wishes to process payments on behalf of its merchants, it makes an agreement with an acquiring bank. The master merchant account is issued by the acquirer, and the PayFac uses it to execute all transactions for the sub-merchant. The buyer’s money is sent directly from the PayFac to the sub-merchant account.
How can a PayFac generate revenue?
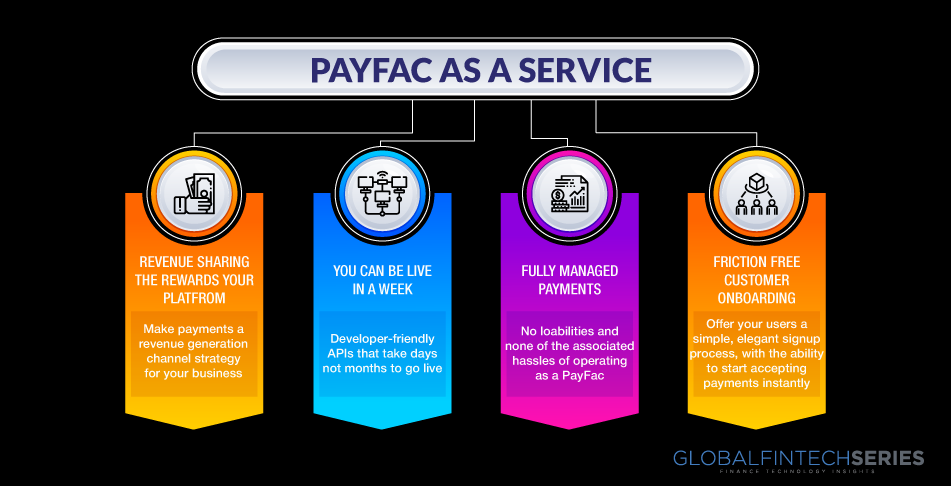
PayFacs also generates income by processing payments on the site in addition to selling their software. Become a vital component of your client’s business: Consumers may be able to get by without your software on their own, but by boosting the services you offer, you make it more difficult for them to stop using it.
Latest Read: A Closer Look At Integrated Document Management And Accounts Payable Software
1950-1990: The advent of the credit card and merchant services period
After the emergence of credit cards in the 1950s and the arrival of POS terminals in the 1980s, it was the responsibility of Acquiring Banks to locate merchants, try and convince them to accept credit cards, examine and approve their credit applications, and then onboard them with the required hardware, systems, and procedures.
From the late 1990s to the present, Gateways have fueled internet trade.
A couple of crucial dates in the birth of e-commerce: Amazon was formed in 1994 and eBay a year later in 1995. Later came Authorize.net in 1994, CyberSource and DataCash in 1996, and Bibit in 1997.The initial payment gateways on the market that permitted merchants to expand their companies online included Authorize.net, CyberSource, DataCash, and Bibit. Merchants could either sign up for one directly or discover one supported by their Acquiring Bank through these independent gateways, which were not (at the time) linked with any ISO or Acquiring Bank.
PayFacs has been streamlining merchant services since 2010
Two of the most renowned PayFacs, Square and Stripe, were launched in 2009. The first formal PayFac schemes were introduced by MasterCard and Visa in 2010 and 2011, respectively, throughout the next two years.
So what makes the PayFac so Unique?
The new “merchant”: To be accepted as a merchant, the PayFac establishes a connection with an acquiring bank and requests a Merchant ID from the card networks. Acquiring sub-merchants: The PayFac then acquires clients; as the “master merchant,” the PayFac’s clients are its “sub-merchants.” The PayFac clearly stands between the Acquiring Bank and the sub-merchant in contrast to the ISO model, where the ISO resells merchant services as an extension of/on behalf of the Acquiring Bank. The PayFac is in charge of underwriting its sub-merchants because it has a merchant relationship with the Acquiring Bank (as well as Know Your Customer, Anti-Money Laundering, and other compliance checks). The sub-merchants can become approved sub-merchants in a matter of hours or days as opposed to weeks or months because they do not have to go through the conventional bank underwriting process. Portfolio diversification: By signing up smaller sub-merchants much more quickly, The PayFac may be taking on some extra credit risk. However, the PayFac aggregates at scale and so mitigates the increased credit risk through diversification. Funds flow: During the settlement process, the PayFac, acting as the master merchant, receives money from the Acquiring Bank. The PayFac subsequently redistributes money to its affiliate merchants and manages any subsequent chargebacks or refunds. Technology: PayFacs provides its sub-merchants with proprietary technological solutions in the form of hardware, software, and/or gateways. For instance, Toast offers a suite of restaurant management software, Square offers its integrated POS system, and Stripe gives its code and APIs. PayFacs can offer a comprehensive merchant services solution because they also offer these technological components.
Latest Read: 10 Of The Best Stock Market Podcasts
Payment Facilitator: Advantages
- Using payment facilitation, a platform can collect payments as soon as 15 minutes after an application has been submitted and rapidly onboard new users.
- A payment facilitator offers sub-merchants extra payment processing benefits, such as seamless payment integration options, in addition to expediting the enrollment and onboarding procedure.
- One of the advantages of employing a facilitator is that all major card networks and types, including ACH, eCheck, and even Electronic Bill Pay Presentment (EBPP), can be enabled through a single interface.
- These networks and types include Visa, Mastercard, Discover, and Amex. Businesses are further encouraged to partner with a payment facilitator by having a transparent, simple cost structure that allows them to better manage their budgets and prevents any unexpected fees.
- Because they can take care of a lot of the hassles associated with Know Your Customer (KYC) standards, Anti-Money Laundering (AML) laws, underwriting, and application processing, PayFacs are especially beneficial for small businesses.
- Together with the hardware, software, and APIs they offer for payment processing, PayFac also offers integrated fraud prevention solutions and chargeback management services that merchants may take advantage of.
Additional perks of PayFac:
1. Offers a quick and simple onboarding procedure
Dealing with a facilitator makes it unnecessary to use conventional payment providers. In a conventional arrangement, merchants must apply for a MID and sign a direct contract with a sponsor bank. Usually, this requires a lot of documentation, which might take days or even weeks to finish. Payment facilitation speeds up the onboarding and underwriting process for merchants, as was already indicated. Usually, on the same day, they can finish their application and open a real account. Working together with a payment facilitator gives you the shared ability to easily set up sub-merchants. Since they don’t need to fill out paperwork or submit supporting papers to set up their account, this streamlines the process of acquiring new clients.
2. The PayFac controls who can access the platform.
Sub-merchants are not tied to a contract with the bank’s terms because the facilitator enters into a direct agreement with the bank. As a result, the PayFac can manage its sub-merchants with more flexibility. This also implies that the facilitator is in charge of hiring application screening. Underwriting is the procedure used to prevent high-risk companies from being accepted as sub-merchants.
3. Create a new source of income for your company.
A payment facilitator will increase your options for earning money. With an ISO, the revenue is divided into three parts because the acquiring bank keeps a portion of it. Yet since the acquiring bank is no longer a factor when using a payment facilitator, you’ll make more money from the offer. The income split between you and the payment facilitator is thus increased.
4. Improved platform value
Facilitators of payments improve your platform for your users. EMV, mobile payment choices, and contactless payment solutions are just a few of the new possibilities brought on by the combination of software and money. Due to these digital payment methods, there are additional prospects for NFC (Near Field Communication) based loyalty programs to offer a generally improved consumer experience.